Electrical Distribution Systems
WIRING SCHEMES AND GROUNDING
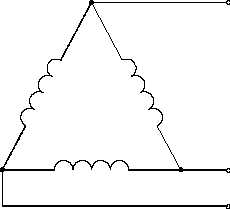
The upper diagram depicts the
Figure 17 3-Wire, Three-Phase Delta Scheme
ungrounded Delta, normally
confined
to
protected
environments such as fully
enclosed ducts or overhead
transmission lines that cannot
b e
r e a c h e d
w i t h o u t
extraordinary
means.
Each
conductor’s ground voltage is
equal to the full phase voltage
of the system.
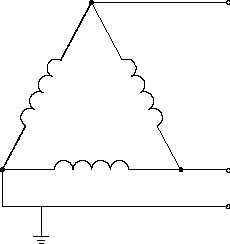
The lower diagram shows a
ground point affixed to one
corner of the Delta, which
effectively lowers one phase’s
voltage reference to ground to
zero, but retains a phase-to-
phase voltage potential. The
corner-grounded phase acts in
much the same way as the
grounded neutral of the single-
phase Edison system, carrying
current and maintaining ground
potential.
The corner-grounded Delta
system
has
an
obvious
economy in wiring costs, and
the grounded phase can be
used to physically protect the
other
two
phases
from
accidental grounding or lightning strikes in outdoor settings. This system is rarely used for low
voltage (under 600 V), however, because of the absence of a safety ground required by many
facilities for circuits involving potential worker contact.
4-Wire, Three-Phase Delta System
The 4-wire, three-phase Delta system combines the ungrounded Delta discussed above for three-
phase loads with the convenience of the Edison system for single-phase loads. As depicted in
the example illustration in Figure 18, one side of the Delta has a grounded-neutral conductor
connected to a center tap winding on one phase.
Rev. 0
Page 25
ES-15