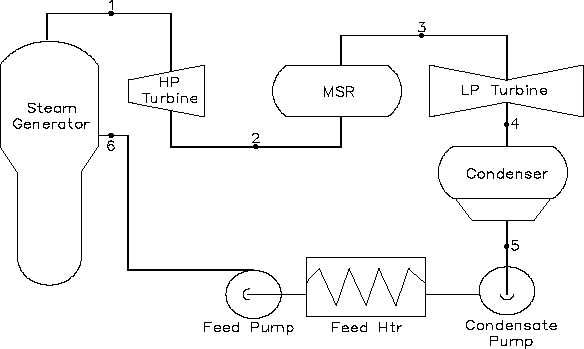
Thermodynamics
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
4-5:
Steam exhaust from the turbine is condensed in the condenser in which heat is
transferred to the cooling water under a constant vacuum condition.
5-6:
The feedwater is compressed as a liquid by the condensate and feedwater pump
and the feedwater is preheated by the feedwater heaters.
6-1:
Heat is added to the working fluid in the steam generator under a constant
pressure condition.
Figure 35 Typical Steam Cycle
The previous cycle can also be represented on a T-s diagram as was done with the ideal Carnot
and Rankine cycles. This is shown in Figure 36. The numbered points on the cycle correspond
to the numbered points on Figure 36.
It must be pointed out that the cycle we have just shown is an ideal cycle and does not exactly
represent the actual processes in the plant. The turbine and pumps in an ideal cycle are ideal
pumps and turbines and therefore do not exhibit an increase in entropy across them. Real pumps
and turbines would exhibit an entropy increase across them.
Rev. 0
Page 91
HT-01