PRINCIPLES OF CONTROL SYSTEMS
Process Controls
Terminology
A control system is a system of integrated elements whose function is to maintain a process
variable at a desired value or within a desired range of values. The control system monitors a
process variable or variables, then causes some action to occur to maintain the desired system
parameter. In the example of the central heating unit, the system monitors the temperature of
the house using a thermostat. When the temperature of the house drops to a preset value, the
furnace turns on, providing a heat source. The temperature of the house increases until a switch
in the thermostat causes the furnace to turn off.
Two terms which help define a control system are input and output. Control system input is the
stimulus applied to a control system from an external source to produce a specified response from
the control system. In the case of the central heating unit, the control system input is the
temperature of the house as monitored by the thermostat.
Control system output is the actual response obtained from a control system. In the example
above, the temperature dropping to a preset value on the thermostat causes the furnace to turn
on, providing heat to raise the temperature of the house.
In the case of nuclear facilities, the input and output are defined by the purpose of the control
system. A knowledge of the input and output of the control system enables the components of
the system to be identified. A control system may have more than one input or output.
Control systems are classified by the control action, which is the quantity responsible for
activating the control system to produce the output. The two general classifications are open-loop
and closed-loop control systems.
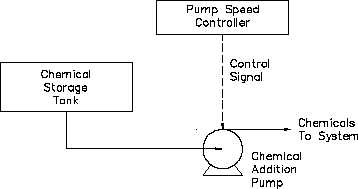
An open-loop control system is
Figure 1 Open-Loop Control System
one in which the control action is
independent of the output.
An
example of an open-loop control
system is a chemical addition
pump with a variable speed control
(Figure 1).
The feed rate of
chemicals that maintain proper
chemistry
of
a
system
is
determined by an operator, who is
not part of the control system. If
the chemistry of the system
changes, the pump cannot respond
by adjusting its feed rate (speed)
without operator action.
IC-07
Page 2
Rev. 0