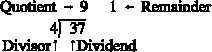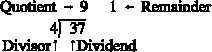Review of Introductory Mathematics
FOUR BASIC ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS
Dividing Whole Numbers
Division is the process of determining how many times one number is contained in another
number. When numbers are divided, the result is the quotient and a remainder. The remainder
is what remains after division. The number divided by another number is called the dividend;
the number divided into the dividend is called the divisor. Division is indicated by any of the
following:
a division sign (÷)
a division sign (
)
a horizontal line with the dividend above the line and the divisor below the line
#
#
a slanting line a/b meaning a divided by b
Thus, the relationship between the dividend, divisor, and quotient is as shown below:
37
Dividend
÷ 4
Divisor
9
Quotient
1
Remainder
Unlike multiplication, the division process is neither associative nor commutative.
The
commutative law for multiplication permitted reversing the order of the factors without changing
the product. In division the dividend and divisor cannot be reversed.
Using the equation form:
a ÷ b =/ b ÷ a
(1-6)
For example, the quotient of 18 ÷ 6 is not the same as the quotient of 6 ÷ 18. 18 divided by 6
equals 3; 6 divided by 18 equals 0.33.
Rev. 0
Page 13
MA-01