POLYMORPHISM
DOE-HDBK-1017/1-93
Structure of Metals
POLYMORPHISM
Metals are capable of existing in more than one form at a time. This chapter will
discuss this property of metals.
EO 1.7
DEFINE the term polymorphism.
EO 1.8
IDENTIFY the ranges and names for the three polymorphism
phases associated with uranium metal.
EO 1.9
IDENTIFY the polymorphism phase that prevents pure
uranium from being used as fuel.
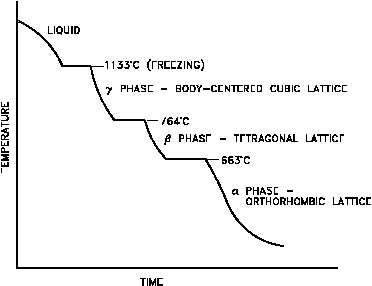
Polymorphism is the property
Figure 5 Cooling Curve for Unalloyed Uranium
or ability of a metal to exist in
two or more crystalline forms
depending upon temperature
and composition. Most metals
and metal alloys exhibit this
property. Uranium is a good
example of a metal that
exhibits
polymorphism.
Uranium metal can exist in
three
different
crystalline
structures.
Each structure
exists at a specific phase, as
illustrated in Figure 5.
1.
The alpha phase, from room temperature to 663C
2.
The beta phase, from 663C to 764C
3.
The gamma phase, from 764C to its melting point of 1133C
MS-01
Page 12
Rev. 0