POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
DOE-HDBK-1018/1-93
Pumps
Lobe Type Pump
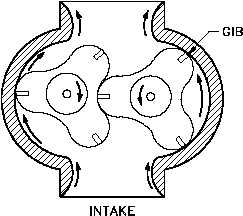
Figure 16 Lobe Type Pump
The lobe type pump shown in Figure 16
is another variation of the simple gear
pump. It is considered as a simple gear
pump having only two or three teeth per
rotor; otherwise, its operation or the
explanation of the function of its parts is
no different.
Some designs of lobe
pumps are fitted with replaceable gibs,
that is, thin plates carried in grooves at
the extremity of each lobe where they
make contact with the casing. The gib
promotes tightness and absorbs radial
wear.
Screw-Type Positive Displacement Rotary Pump
There are many variations in the design of the screw type positive displacement, rotary
pump. The primary differences consist of the number of intermeshing screws involved,
the pitch of the screws, and the general direction of fluid flow. Two common designs are
the two-screw, low-pitch, double-flow pump and the three-screw, high-pitch, double-flow
pump.
Two-Screw, Low-Pitch, Screw Pump
The two-screw, low-pitch, screw pump consists of two screws that mesh with close
clearances, mounted on two parallel shafts. One screw has a right-handed thread, and
the other screw has a left-handed thread. One shaft is the driving shaft and drives the
other shaft through a set of herringbone timing gears. The gears serve to maintain
clearances between the screws as they turn and to promote quiet operation. The
screws rotate in closely fitting duplex cylinders that have overlapping bores. All
clearances are small, but there is no actual contact between the two screws or between
the screws and the cylinder walls.
ME-03
Rev. 0
Page 24