FILTERS AND STRAINERS
DOE-HDBK-1018/2-93
Miscellaneous Mechanical Components
If too much filter medium is used, the layer that builds up on the septums will bridge the area
between the septums. When the filter is backwashed, these bridges are usually not removed.
Therefore the bridging continues, and the filter runs become progressively shorter. Eventually,
the filter must be opened and the filter medium must be removed manually.
Precoat filters are much more complicated than cartridge filters, and the equipment required is
much more expensive to install and maintain. The major advantage of precoat filters is the
remote operation, which eliminates the physical handling of highly radioactive filter cartridges.
Deep-Bed Filters
Deep-bed filters are usually found only in makeup water systems, where they are used to filter
water after it has been treated in a clarifier. They are used to remove organic matter, chlorine,
and very fine particulate matter.
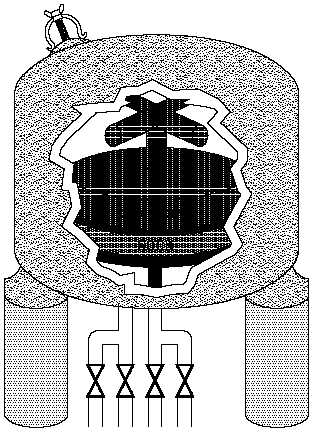
A deep-bed filter is based on a support
Figure 22 Deep-Bed Filter
screen (decking), which is mounted a
few inches above the bottom of the
tank.
The screen is perforated to
allow water to flow through it. A
coarse, aggregate layer of crushed rock
or large lumps of charcoal is placed
on top of the screen, and the deep bed
itself (2 to 4 feet of granular anthracite
or charcoal) is placed on top of the
aggregate. The filter is sized so that
there is 1 to 2 feet of "free board"
above the deep bed.
When the filter is in service, raw
water is pumped in through a pipe that
feeds a distribution pipe above the
deep bed. The water is filtered as it
percolates down through the granules.
(Charcoal granules will filter out
organic matter, chlorine, and fine
particulates, while anthracite granules
remove only the particulates.) The
water collects in the bottom of the
tank, below the support screen, and
leaves the filter through a pipe in the
bottom of the filter vessel.
ME-05
Rev. 0
Page 44