VALVE FUNCTIONS AND BASIC PARTS
DOE-HDBK-1018/2-93
Valves
Stem
The stem, which connects the actuator and disk, is responsible for positioning the disk.
Stems are typically forged and connected to the disk by threaded or welded joints. For
valve designs requiring stem packing or sealing to prevent leakage, a fine surface finish
of the stem in the area of the seal is necessary. Typically, a stem is not considered a
pressure boundary part.
Connection of the disk to the stem can allow some rocking or rotation to ease the
positioning of the disk on the seat. Alternately, the stem may be flexible enough to let
the disk position itself against the seat. However, constant fluttering or rotation of a
flexible or loosely connected disk can destroy the disk or its connection to the stem.
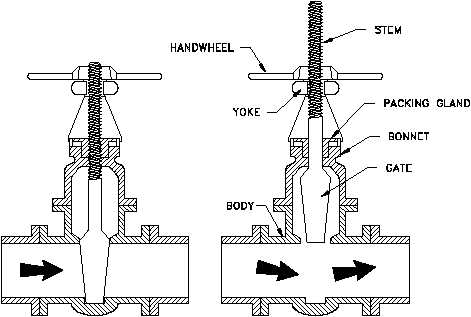
Two types of valve stems are rising stems and nonrising stems. Illustrated in Figures 2
and 3, these two types of stems are easily distinguished by observation. For a rising stem
valve, the stem will rise above the actuator as the valve is opened. This occurs because
the stem is threaded and mated with the bushing threads of a yoke that is an integral part
of, or is mounted to, the bonnet.
Figure 2 Rising Stems
ME-04
Rev. 0
Page 4