vp
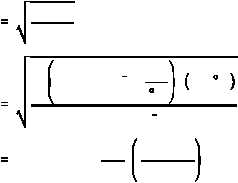
2 k T
m
2
1.38 x 1016erg
K
533 K
1.66 x 1024 g
2.977 x 105cm
sec
1 m
100 cm
2977
m
sec
NEUTRON FLUX SPECTRUM
DOE-HDBK-1019/1-93
Reactor Theory (Neutron Characteristics)
NP-02
Page 36
Rev. 0
b)
Calculate the most probable velocity for 260 C using Equation (2-13).
From these calculations it is evident that the most probable velocity of a thermal neutron
increases as temperature increases. The most probable velocity at 20 C is of particular
importance since reference data, such as nuclear cross sections, are tabulated for a neutron
velocity of 2200 meters per second.