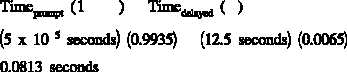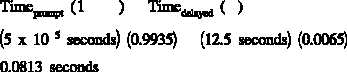Reactor Theory (Neutron Characteristics)
DOE-HDBK-1019/1-93
PROMPT AND DELAYED NEUTRONS
Rev. 0
Page 31
NP-02
On the other hand, the average generation time for the six delayed neutron groups is the total
time from the birth of the fast neutron to the emission of the delayed neutron. Again, three time
intervals are involved: (a) the time it takes a fast neutron to slow down to thermal energy,
(b) the time the thermal neutron exists prior to absorption, and (c) the average time from neutron
absorption to neutron emission by the six precursor groups. The average time for decay of
precursors from uranium-235 is 12.5 seconds. The other terms in the delayed neutron
generation time are insignificant when compared to this value, and the average delayed neutron
generation time becomes 12.5 seconds.
A neutron generation time in the range of 10 seconds to 10 seconds or faster could result in
-4
-5
very rapid power excursions, and control would not be possible without the dependence upon
delayed neutrons to slow down the rate of the reaction. The average generation time, and hence
the rate that power can rise, is determined largely by the delayed neutron generation time. The
following equation shows this mathematically.
(2-12)
Example:
Assume a prompt neutron generation time for a particular reactor of 5 x 10 seconds and
-5
a delayed neutron generation time of 12.5 seconds. If is 0.0065, calculate the average
generation time.
Solution:
This example demonstrates the effect delayed neutrons have on the neutron generation time and
thus reactor control. If a reactor were to be operated in a sustained chain reaction using only
prompt neutrons ( = 0), the generation time from the previous example would be about
5 x 10 seconds. However, by operating the reactor such that a 0.0065 fraction of neutrons are
-5
delayed, the generation life time is extended to 0.0813 seconds, providing time for adequate
operator control. Therefore, although only a small fraction of the total neutron population,
delayed neutrons are extremely important to the control and maintenance of a sustained fission
chain reaction.
Summary
The important information in this chapter is summarized on the following page.