BATTERY THEORY
Batteries
Discharge and Charging of Lead-Acid Battery
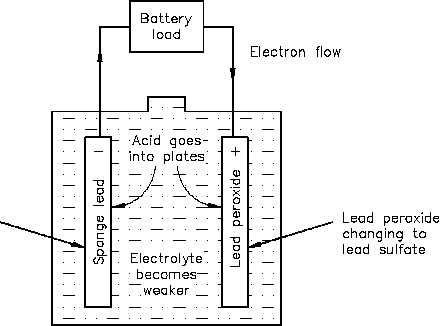
In a lead-acid battery, two types of lead are acted upon electro-chemically by an electrolytic
solution of diluted sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The positive plate consists of lead peroxide (PbO2), and
the negative plate is sponge lead (Pb), shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4 Chemical Action During Discharge
When a lead-acid battery is discharged, the electrolyte divides into H2 and SO4. The H2 will
combine with some of the oxygen that is formed on the positive plate to produce water (H2O),
and thereby reduces the amount of acid in the electrolyte. The sulfate (SO4) combines with the
lead (Pb) of both plates, forming lead sulphate (PbSO4), as shown in Equation (4-1).
(4-1)
PbO2
Pb
2H2SO4
discharge
2PbSO4
2H2O
ES-04
Page 6
Rev. 0