Batteries
BATTERY THEORY
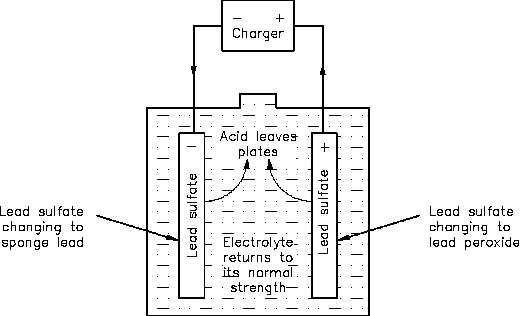
As a lead-acid battery is charged in the reverse direction, the action described in the discharge
is reversed. The lead sulphate (PbSO4) is driven out and back into the electrolyte (H2SO4). The
return of acid to the electrolyte will reduce the sulphate in the plates and increase the specific
gravity. This will continue to happen until all of the acid is driven from the plates and back into
the electrolyte, as shown in Equation (4-2) and Figure 5.
Figure 5 Chemical Action During Charging
(4-2)
PbO2
Pb
2H2SO4
charge
2PbSO4
2H2O
As a lead-acid battery charge nears completion, hydrogen (H2) gas is liberated at the negative
plate, and oxygen (O2) gas is liberated at the positive plate. This action occurs since the charging
current is usually greater than the current necessary to reduce the remaining amount of lead
sulfate on the plates. The excess current ionizes the water (H2O) in the electrolyte. Since
hydrogen is highly explosive, it is necessary to provide adequate ventilation to the battery
whenever charging is in progress. Also, no smoking, electric sparks, or open flames are allowed
near a charging battery.
Rev. 0
Page 7
ES-04