CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS
Fluid Flow
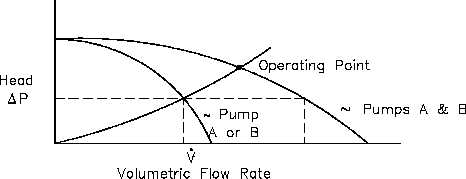
When the system characteristic curve is considered with the curve for pumps in parallel, the
operating point at the intersection of the two curves represents a higher volumetric flow rate than
for a single pump and a greater system head loss. As shown in Figure 12, a greater system head
loss occurs with the increased fluid velocity resulting from the increased volumetric flow rate.
Because of the greater system head, the volumetric flow rate is actually less than twice the flow
rate achieved by using a single pump.
Figure 12 Operating Point for Two Parallel Centrifugal Pumps
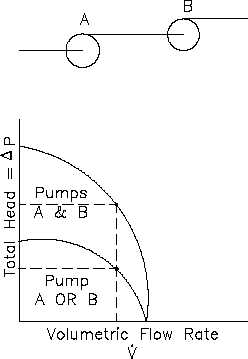
Figure 13 Pump Characteristic Curve for Two Identical Centrifugal
Pumps Used in Series
Centrifugal Pumps in Series
Centrifugal pumps are used in
series to overcome a larger system
head loss than one pump can
compensate for individually. As
illustrated in Figure 13, two
identical
centrifugal
pumps
operating at the same speed with
the same volumetric flow rate
contribute the same pump head.
Since the inlet to the second pump
is the outlet of the first pump, the
head produced by both pumps is
the sum of the individual heads.
The volumetric flow rate from the
inlet of the first pump to the outlet
of the second remains the same.
HT-03
Page 54
Rev. 0