CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS
Fluid Flow
System Characteristic Curve
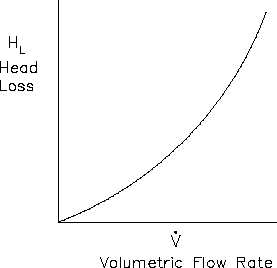
Figure 9 Typical System Head Loss Curve
In the chapter on head loss, it was determined
that both frictional losses and minor losses in
piping systems were proportional to the
square of the flow velocity.
Since flow
velocity is directly proportional to the
volumetric flow rate, the system head loss
must be directly proportional to the square of
the volumetric flow rate.
From this
relationship, it is possible to develop a curve
of system head loss versus volumetric flow
rate. The head loss curve for a typical piping
system is in the shape of a parabola as shown
in Figure 9.
System Operating Point
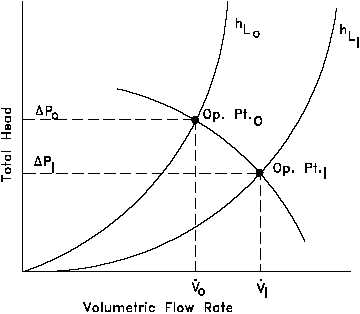
Figure 10 Operating Point for a Centrifugal Pump
The point at which a pump
operates in a given piping system
depends on the flow rate and head
loss of that system. For a given
system, volumetric flow rate is
compared to system head loss on a
system characteristic curve. By
graphing a system characteristic
curve and the pump characteristic
curve on the same coordinate
system, the point at which the
pump must operate is identified.
For example, in Figure 10, the
operating point for the centrifugal
pump in the original system is
designated by the intersection of
the pump curve and the system
curve (hLo).
HT-03
Page 52
Rev. 0