Review of Introductory Mathematics
FOUR BASIC ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS
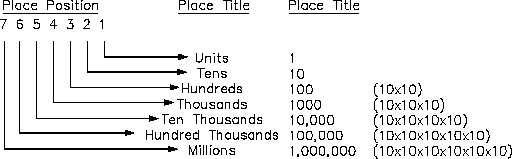
Numbers in the decimal system may be classified as integers or fractions. An integer is a whole
number such as 1, 2, 3, . . . 10, 11, . . . A fraction is a part of a whole number, and it is
expressed as a ratio of integers, such as 1/2, 1/4, or 2/3.
An even integer is an integer which can be exactly divided by 2, such as 4, 16, and 30. All other
integers are called odd, such as 3, 7, and 15. A number can be determined to be either odd or
even by noting the digit in the units place position. If this digit is even, then the number is even;
if it is odd, then the number is odd. Numbers which end in 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 are even, and numbers
ending in 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 are odd. Zero (0) is even.
Examples:
Determine whether the following numbers are odd or even: 364, 1068, and 257.
Solution:
1.
364 is even because the right-most digit, 4, is an even number.
2.
1068 is even because the right-most digit, 8, is an even number.
3.
257 is odd because the right-most digit, 7, is an odd number.
Adding Whole Numbers
When numbers are added, the result is called the sum. The numbers added are called addends.
Addition is indicated by the plus sign (+). To further explain the concept of addition, we will
use a number line to graphically represent the addition of two numbers.
Example:
Add the whole numbers 2 and 3.
Solution:
Using a line divided into equal segments we can graphically show this addition.
Rev. 0
Page 7
MA-01