Higher Concepts of Mathematics
CALCULUS
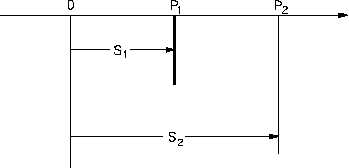
Figure 2 Motion Between Two Points
If the time recorded by a clock, when the object is at position P1 is t1, and if the time when the
object is at position P2 is t2, then the average velocity of the object between points P1 and P2
equals the distance traveled, divided by the elapsed time.
(5-1)
Vav
S2
S1
t2
t1
If positions P1 and P2 are close together, the distance traveled and the elapsed time are small.
The symbol D, the Greek letter delta, is used to denote changes in quantities. Thus, the average
velocity when positions P1 and P2 are close together is often written using deltas.
(5-2)
Vav
DS
Dt
S2
S1
t2
t1
Although the average velocity is
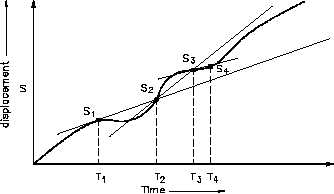
Figure 3 Displacement Versus Time
often an important quantity, in
many cases it is necessary to know
the velocity at a given instant of
time.
This velocity, called the
instantaneous velocity, is not the
same as the average velocity,
unless the velocity is not changing
with time.
Using the graph of displacement,
S, versus time, t, in Figure 3, we
will try to describe the concept of
the derivative.
Rev. 0
Page 31
MA-05