Fundamentals of Chemistry
DOE-HDBK-1015/1-93
CHEMICAL BONDING
Rev. 0
CH-01
Page 31
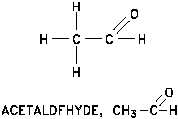
Figure 16 Aldehyde
Aldehydes
Aldehydes are one of the oxidation products of the alcohols.
Each of these compounds contain a carbonyl group (a carbon
atom double bonded to an oxygen atom) as illustrated in
Figure 16.
The term "aldehyde" is a contraction of the term "alcohol
dehydrogenation" indicating that two hydrogen atoms are
removed from an end carbon when aldehydes are prepared
from primary alcohols. The functional group (-C=O) is always
at the end of the carbon chain.
Basic Chemical Laws
As previously stated, all matter is composed of atoms that which are capable of uniting to
form chemical compounds. The various forms of matter can be summarized from a chemical
point of view as follows.
1.
Molecules are groups or clusters of atoms held together firmly by means of
chemical bonding. There are two general types of molecules.
a.
Molecule of an element - Two single atoms of the same element, in
certain cases, can become fastened to one another by a chemical bond to
form a molecule. Examples of this are hydrogen (H ), oxygen (O ), and
2
2
bromine (Br ). Most gaseous elements exist as molecules of two atoms.
2
b.
Molecules of a compound - A compound contains at least two different
kinds of atoms. Molecules are the ultimate particles of chemical
compounds. Examples of compounds are hydrogen chloride (HCl),
water (H O), methane (CH ), and ammonia (NH ).
2
4
3
2.
Elements are substances that cannot be decomposed by ordinary types of
chemical change nor made by chemical union.
3.
Compounds are substances containing more than one constituent element and
having properties different from those of the individual elements. The
composition of a specific compound is always definite.
4.
Mixtures consist of two or more substances intermingled with no constant
percentage composition. Each component retains its original properties.