CHEMICAL BONDING
DOE-HDBK-1015/1-93
Fundamentals of Chemistry
CH-01
Rev. 0
Page 28
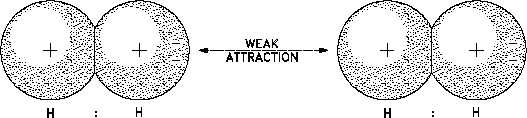
Figure 10 Van der Waals Forces
Van der Waals forces are small compared to the forces of chemical bonding and are significant
only when the molecules are very close together.
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is defined as the chemistry of carbon compounds. The compounds of carbon
are in forms of living things and in synthetic fabrics and plastics. Organic chemistry is so broad
a topic that it is usually subdivided into smaller areas. How the carbon is combined and what
it is combined with determines the subdivision for a particular compound. These subdivisions
are referred to as families or classes.
The carbon atoms can combine to form straight chains, rings, or branched chains. The bonds
between carbon atoms can be single, double, triple or a combination of these. Other atoms (H,
O, N, S, P) and the halogens can be attached to the carbon atoms to yield derivatives.
The large family of organic compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen are called
hydrocarbons. These can be further divided into two broad classes, aliphatic (fatty) and
aromatic (fragrant).
Aliphatic hydrocarbons are divided into two categories, saturated and unsaturated and into
subdivisions alkanes, alkenes, and alkynes. These subdivisions reflect the type of bond between
the carbon atoms.
Alkanes
Alkanes are saturated compounds which have single bonds between carbon atoms and contain
the maximum number of hydrogen atoms possible. Each carbon is flanked by four covalent
bonds and each hydrogen atom shares one pair of electrons with a carbon atom, as illustrated
in Figure 11.