Atomic and Nuclear Physics
DOE-HDBK-1019/1-93
MODES OF RADIOACTIVE DECAY
Rev. 0
Page 25
NP-01
Figure 9 Orbital Electron Capture
Positively charged electrons (beta-plus) are known as positrons. Except for sign, they are nearly
identical to their negatively charged cousins. When a positron, represented as e, , or simply as
+1
+1
0
0
e or
, is ejected from the nucleus, the atomic number is decreased by one and the mass number
+
+
remains unchanged. A proton has been converted to a neutron. An example of a typical positron
(beta-plus) decay is shown below.
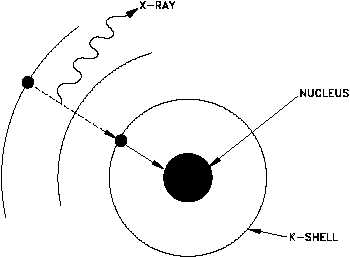
Electron Capture (EC, K-capture)
Nuclei having an excess of protons may capture an electron from one of the inner orbits which
immediately combines with a proton in the nucleus to form a neutron. This process is called electron
capture (EC). The electron is normally captured from the innermost orbit (the K-shell), and,
consequently, this process is sometimes called K-capture. The following example depicts electron
capture.
A neutrino is formed at the same
time that the neutron is formed, and
energy carried off by it serves to
conserve momentum. Any energy
that is available due to the atomic
mass
of
the
product
being
appreciably less than that of the
parent will appear as gamma
radiation. Also, there will always
be characteristic x-rays given off
when an electron from one of the
higher energy shells moves in to fill
the vacancy in the K-shell.
Electron
capture
is
shown
graphically in Figure 8.
Electron capture and positron
emission result in the production of
the same daughter product, and
they exist as competing processes.
For positron emission to occur, however, the mass of the daughter product must be less than the
mass of the parent by an amount equal to at least twice the mass of an electron. This mass difference
between the parent and daughter is necessary to account for two items present in the parent but not
in the daughter. One item is the positron ejected from the nucleus of the parent. The other item is
that the daughter product has one less orbital electron than the parent. If this requirement is not met,
then orbital electron capture takes place exclusively.