OPERATION AND CONSTRUCTION
DOE-HDBK-1084-95
Lead-Acid Storage Batteries
Batteries
Page 14
Rev. 0
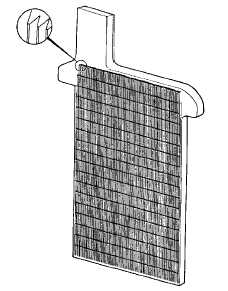
Figure 4. Typical planté plate.
Negative and Positive Plate Construction Methods
The simplest method for the construction of lead-acid battery electrodes is the planté plate,
named after the inventor of the lead-acid battery. A planté plate is merely a flat plate
composed of pure lead. Since the capacity of a lead-acid battery is proportional to the surface
area of the electrodes that is exposed to the electrolyte, various schemes are employed to
increase the surface area of the electrodes per unit volume or weight. Planté plates are
grooved or perforated to increase their surface area. A typical planté plate is shown in Figure
4.
The most commonly used method to increase surface area is to make the active material into a
paste that acts like a sponge where the electrolyte fills all the pores. The paste, or active
material, is mounted into a frame or grid structure that mechanically supports it and serves as
the electrical conductor carrying the current during both the charge and discharge cycle. The
most commonly used plate today is the pasted plate, also known as the flat plate. This grid
structure is a lattice-work that resembles the cross section of a honeycomb, with the paste
filling all of the rectangular windows on the structure. Figure 5 shows a typical construction
of a pasted plate grid. The flat plate construction is used as the negative electrode plate in
almost all cases, and serves as the positive plate in most standby applications.