OPERATION AND CONSTRUCTION
DOE-HDBK-1084-95
Lead-Acid Storage Batteries
Batteries
Page 18
Rev. 0
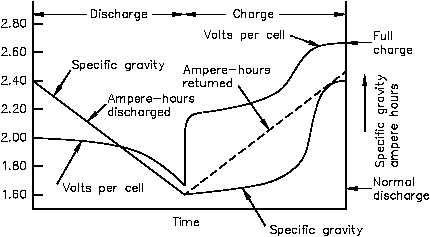
Figure 8. Changes in voltage and specific gravity during charge and discharge.
Therefore, during fully charged steady-state operation and on discharge, measurement of the
specific gravity of the electrolyte provides an approximate indication of the state of charge of
the cell. The downward sloping line for the specific gravity during discharge is approximated
by the equation below:
Specific gravity = cell open-circuit voltage - 0.845
(5)
or
Cell open circuit voltage = specific gravity + 0.845.
(6)
The above equations permit electrical monitoring of approximate specific gravity on an
occasional basis. As mentioned earlier, specific gravity measurements cannot be taken on
sealed lead-acid batteries. Measurement of the cell open-circuit voltage has been used as an
indicator of the state of charge of a sealed battery. More reliable methods for determining the
state of charge of sealed batteries are under development.
The specific gravity decreases during the discharging of a battery to a value near that of pure
water and it increases during a recharge. The battery is considered fully charged when
specific gravity reaches it's highest possible value.
Specific gravity does, of course, vary with temperature and the quantity of electrolyte in a
cell. When the electrolyte is near the low-level mark, the specific gravity is higher than
nominal and drops as water is added to the cell to bring the electrolyte to the full level. The