Days in storage at 25- C
Lead-calcium grid
Lead-Acid Storage Batteries
DOE-HDBK-1084-95
OPERATON AND CONSTRUCTION
Rev. 0
Page 17
Batteries
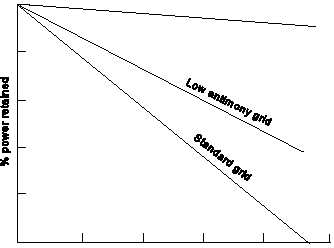
Figure 7. Self-discharge rates of three grid materials.
by long-term overcharging, which is common to UPS and other batteries
on constant-float changing. Grids may grow in size sufficiently to cause
buckling or rupture of their containers.
Another type of grid alloy is lead-selenium. In reality, this battery is actually a low
lead-antimony grid with a slight amount of selenium. Lead-selenium has characteristics
that fall somewhere between lead-calcium and lead-antimony.
When pure lead is mixed with an alloy there may be undesirable characteristics
introduced in the performance of the battery. Modern day battery manufacturers try to
reduce the amount of antimony and calcium by introducing doping agents such as
selenium, cadmium, tin, and arsenic. When batteries containing arsenic and antimony
are charged (especially overcharged) the poisonous gases arsine (AsH ) and stibine
3
(SbH ) may be released. This is discussed further in the paragraphs devoted to
3
charging.
Specific Gravity
One of the key parameters of battery operation is the specific gravity of the electrolyte.
Specific gravity is the ratio of the weight of a solution to the weight of an equal volume of
water at a specified temperature. Specific gravity is used as an indicator of the state of charge
of a cell or battery. However, specific gravity measurements cannot determine a battery's
capacity. During discharge, the specific gravity decreases linearly with the ampere-hours
discharged as indicated in Figure 8.