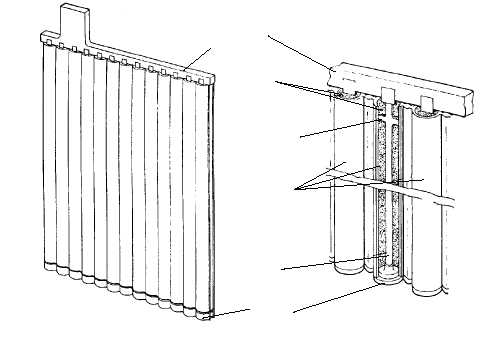
Connector
bus
Active
material
Centering
projections
Porous
separators
Axial
lead
current
collector
End cap
OPERATION AND CONSTRUCTION
DOE-HDBK-1084-95
Lead-Acid Storage Batteries
Batteries
Page 16
Rev. 0
Figure 6. Typical construction of a tubular plate.
The two most common alloys used today to harden the grid are antimony and calcium.
Batteries with these types of grids are sometimes called "lead-antimony" and "lead-
calcium" batteries. Tin is added to lead-calcium grids to improve cyclability. The
major differences between batteries with lead-antimony and lead-calcium grids are as
follows:
1.
Lead-antimony batteries can be deep cycled more times than lead-
calcium batteries.
2.
Flooded lead-antimony batteries require more frequent maintenance as
they near end-of-life since they use an increasing amount of water and
require periodic equalization charges.
3.
Lead-calcium batteries have lower self-discharge rates as shown in
Figure 7 and therefore, will draw less current while on float charge than
lead-antimony batteries.
4.
Lead-calcium positive plates may grow in length and width because of
grid oxidation at the grain boundaries. This oxidation is usually caused