Radiation Detectors
IONIZATION CHAMBER
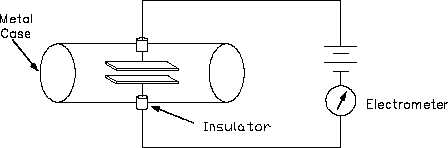
The plates in an ionization chamber are normally enclosed in metal, as shown by Figure 16.
Figure 16 Ionization Chamber
This metal chamber serves to shield the plates from outside electric fields and to contain the air
or other gas. Gamma rays have very little trouble in penetrating the metal walls of the chamber.
Beta particles and alpha particles, however, are stopped by the metal wall. For alpha and beta
particles to be detected, some means must be provided for a thin wall or "window." This
window must be thin enough for the alpha and beta particles to penetrate. However, a window
of almost any thickness will prevent an alpha particle from entering the chamber.
Neutrons can also be detected by an ionization chamber. As we already know, neutrons are
uncharged; therefore, they cause no ionizations themselves. If the inner surface of the ionization
chamber is coated with a thin coat of boron, the following reaction can take place.
10
1
7
4
B
n Li
He
5e
5
0
3
2
A neutron is captured by a boron atom, and an energetic alpha particle is emitted. The alpha
particle causes ionization within the chamber, and ejected electrons cause further secondary
ionizations.
Another method for detecting neutrons using an ionization chamber is to use the gas boron tri-
fluoride (BF3) instead of air in the chamber. The incoming neutrons produce alpha particles
when they react with the boron atoms in the detector gas. Either method may be used to detect
neutrons in nuclear reactor neutron detectors.
Rev. 0
Page 31
IC-06